COMPLETED QUANTUM MECHANICAL THEORY (CQMT)
Nimit Theeraleekul B. Eng. (Communication)
(April 17, 2008, 1st revision Oct. 1, 2011)
Abstract: Quantum mechanics is one of the most important theories in modern physics, despite of their predictability and accuracy; it is facing with crucial philosophic problems. Indeed the problems could be solved, and the theory could be improved by using “Vacuum Mechanics” i.e. the mechanism of vacuum medium concept!
Content: 1) Background. 2) Introduction. 3) Philosophy behind natural wave. 3.1) Crisis of wave in modern physics. 3.2) Wave-particle duality. 4) Mechanism of particle wave. 5) Particle wave vs. light wave. 6) Mathematical formula for particle wave. 6.1) Original derivation of de Broglie wave. 6.2) Improved de Broglie wave. 7) Better view of Schrödinger equation. 8) Quantum vacuum mechanics. 8.1) Wave collapse interpretation. 8.2) Mechanism of the uncertainty principle. 9) Particle wave or matter wave? 10) Classical mechanics vs. Quantum mechanics. 11) Physical meaning of Plank constant. 12) Is energy continuous or discrete? 13) Is quantum entanglement right or wrong? 13.1) Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox. 13.2) Bell inequality is a mathematical tool. 13.3) Einstein hidden variable vs. quantum mechanics. 14) Problem with hydrogen atom model. 15) Conclusion & Discussion. 16) References.
1) Background. This article is the fourth expanding part of the original article “Vacuum mechanics a New Approach to the Theory of Everything” (VMTE) [1]. There are four most important theories involved in VMTE; Maxwell electromagnetic field theory (EMT), Einstein special theory of relativity (STR), Einstein general theory of relativity (GTR) and Quantum mechanical theory (QMT). Because what has been talked in VMTE is rather a philosophical one, so the first three articles have been expanded into a more scientific detail with the titles “Completed Maxwell electromagnetic field theory” (CEMT), “Completed Einstein special theory of relativity” (CSTR) and “Completed Einstein general theory of relativity” (CGTR) respectively [1].
In VMTE we have started with the fundamental hypothesis that “Vacuum medium is the fabric structure of vacuum space”, and following is with the consequence hypothesis “Electrons and proton are (something like) tiny black holes of vacuum medium”. We have proved the existence of vacuum medium space instead of the conventional empty vacuum space, also showing how “condensed” vacuum medium were formed to be electron and proton, which are the origin of all the material matters existed in the universe!
Also we had shown that “vacuum mechanics” (i.e. the mechanism of vacuum medium) which is the action of vacuum medium or of condensed vacuum medium and the interaction between them, is responsible for all natural phenomena. Then we used it for explaining the unsolved philosophic problems in EMT, STR and GTR and here we will show how to use it to solve the unsolved philosophic problems in QMT either!
2) Introduction. Let us start with Nobel Prize Laureate (in quantum electrodynamics) Richard. P. Feynman word “I think I can safely say nobody understands quantum mechanics” [2], but why? Is it because it was prohibited by God or just due to our ignorance? Here we will find out together!
Another point of view comes from David Bohm, a famous physicist in quantum theory, who said that “Quantum mechanics should be called as quantum nonmechanics” [3]. This is because even through the theory was called “quantum mechanics” which mean that it should be something as “mechanism” of quantum system, but it seems that there is no such thing which could regard as system of separate parts working together according to causal laws!
Could this means that there is no need any mechanism for quantum mechanics? Of course, it should not be that, otherwise it is a magic, not science!
Then it is not surprise that Einstein said that “Quantum mechanics is not a complete theory even though it is correct” [4], and even “What Einstein had in mind by a ‘completion’ of quantum mechanics is not entirely clear, …” [4’]! Anyway we know that a complete theory, by definition, should include with a philosophical idea which explain how the theory work!
And we also know that “Understanding is the progression of science” then it will give us a more confidence that we will not misinterpret the theory and lead to something crazy! Quantum mechanics provide us only mathematic formulas which enable us to calculate a correct result without any deeper understanding, so this is the reason why it is so mysterious that no one could understand it.
Now to improve QMT, we will first point out detail of the main problems that involved. Then we will use the new propose concept of vacuum mechanics (i.e. the mechanism of vacuum medium) to solve the problems. Finally what we will get is “Completed quantum mechanical theory” (CQTM)!
3) Philosophy behind natural wave. Let’s start with the most familiar natural wave that is water wave. When a stone was dropped in a pond, it will disturb the water and creating the circular surface waves and propagate away. Here it is easy to see the mechanism of water wave. First the energy of the falling stone was used to disturb the clam (undisturbed) state of the water. Next, disturbance of the water was oscillated back and forth due to elasticity of water and then creating waves. Finally, the energy was transported away from disturbance point to the rim of the pond by the created waves! So in this sense, we could define that “wave is nature’s mechanism for transporting energy without degradation and without transporting matter” [5]. (Note this definition is given by admitted that energy degradation effects are secondary and that waves are fundamentally conservative phenomena.)
3.1) Crisis of waves in modern physics theories. In classical mechanics, all kind of natural waves which we can see in our daily life are so familiar that there is no need to ask “what is wavy” or “wave of what”? Oscillation of water, vibration of string, vibration of earth quake etc. all is the “wavy of the medium” which is the carrier of the wave involved.
For sound wave, at first sight there is a little doubt because we can not see the medium “air”. Fortunately we still could feel it, and later we had proved that sound wave is the wavy of “air” medium! Actually any physical involved medium can be used; it could be water, string or metal rod. The most crucial point is that there must have something to be the carrier of wave, whether or not we could touch it!
When Maxwell created the electromagnetic field theory, he used elastic solid (aether) to be the carrier of electromagnetic waves. Soon after Einstein had created special theory of relativity then the aether was ignored. And physicists have explained that electromagnetic waves could be propagated by mutual creation between the changing of electric and magnetic field! But the problem is that both electric and magnetic field are created and changing at the same time from one common time varying current source. So how could they create each other? It violates causality! (Please see detail explanation in CEMT.)
Time has pass, physicists seem to forget what the basic criterion for wave is. For example, according to Einstein general theory of relativity, gravity wave was explained to work by the vibration of space-time itself. Unfortunately we could not visualize how empty space-time (without anything) could be act as the mechanism of wave, it seem to be a magic wave rather than a scientific wave!
For Quantum mechanics which is the description of wavelike behavior of atomic particles such as electron, neutron, alpha particle etc., thing get worse! Not only because no one knows what the particle wave is, but also no one knows what its mechanism is! Indeed Max Born whom who gave the correct interpretation of wave function (which was used until now) himself used to call this mysterious wave as ghost field [6]!
Here, armed with vacuum mechanics, we will show that what we called particle wave, actually it is the waves of vacuum medium! It is the different aspect of the same thing as electromagnetic waves (explained in CEMT) and gravity wave (explained in CGTR.) Then ghost wave in QMT will turn to God wave (nature wave), so let’s explore it together.
3.2) Wave–particle duality. Normally when dealing with waves, we usually refer to continuous wave, but there is also a short portion of wave train which was called “wave- packet”. For mechanical wave such as water wave, wave packet could be created by applying a short duration of some disturbance source such as dropping a stone in water. But if we dip a continuous vibrating fork in water, the created waves will be a continuous wave train.
For electromagnetic waves which include radio waves, light wave etc., it seem at first that all are continuous waves. But if we observe carefully, we would found that there are both continuous waves and wave packets. Normally radio waves which are man-made waves are continuous waves, while light waves which are natural waves are wave packets and were called as “photons”. And in one sense we may say that a photon is something like a particle! (Please see detail in CEMT.)
Now let’s look at a particle such as electron which we know that it is obviously a point like particle. Anyway, in some circumstance such as in case of double-slit interference, it reveals itself as if it is wave. So we say that it has a wave-particle duality. This wave-particle duality also occurs in other subatomic particles such as proton, neutron and up to an atom! And these waves which involved with atomic particles were called as “particle waves”.
What really the particle wave is? Nowadays, physicists have used the concept of particle wave successfully, but they still do not know what it is! For example, is an electron composes of particle and wave? Or is it just a particle but also has wave property? In the former, we could not imagine how it is. In the latter, it may be because electron could generate wave, but how?
One interesting point about electron wave is that it will reveal its wave nature only when it is moving! This gives us some hint because it reminds us about the water wave generated by a moving boat. Anyway, water wave can be created only on the condition that there is water to be disturbed by a moving object!
Armed with vacuum medium space, it is easy to understand how electron could generate wave. This is because the moving electron would disturb the surrounding vacuum medium in the same way as a moving boat disturbs the water! Anyway, electron wave is not as simple as water wave, and we will discuss next about its mechanism.
4) Mechanism of particle wave. It is easy to understand particle wave such as electron wave by using method of analogy. Let us start with “surface water waves” created by a moving water beetle as show in the diagram of fig. 1(a). Normally, we are familiar with ship waves which occurred behind the moving ship. But for a small moving object such as a water beetle, the generated waves occur around (and in front of) the moving beetle [7]!
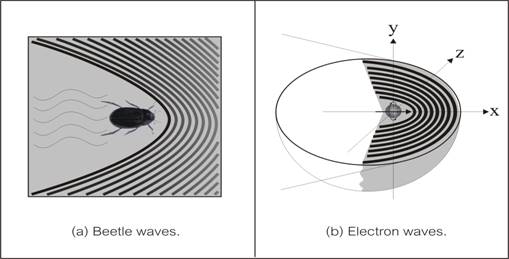
Figure 1 Beetle wave vs. electron wave
In more technical detail of surface water waves, the preceding wave in front of the moving object is capillary wave (wave due to surface tension), while the wave behind the object is gravity wave (wave due to gravitational force). At the first sight it seems that the mentioned water wave phenomena are a simple one, but actually it is very difficult and was study in the advance course of wave!
In summary, beetle wave was classified as linear dispersion wave, so it involves with group velocity of wave. The preceding waves in front of the beetle are the group velocity which contained waves’ energy that move forward and exceed phase velocity of the capillary waves! Normally water beetles typically length is less than 1 cm and they move as fat as 50 – 100 cm/s, then the generated capillary wavelength is 1.7 cm [7’].
Now we return to particle wave such as an electron wave. When an electron moving through vacuum medium (remember that electron is immerged in vacuum medium), it will rotate while disturbing the medium around. The disturbed vacuum medium will adjust itself by creating standing waves in front and around as shown in fig. 1(b). (Note that the diagram shown is a three dimensions which was cut horizontally in x – z plane to show only the lower half part.)
This is the same way as beetle create wave, but why doesn’t electron just only create turbulences around? The answer is that “nature” has her own elegant and effective way to transport energy away via wave mechanism! And of course the wave mechanism is the same thing for any type of waves; it is due to the oscillation from the interchanging action between inertial force and elastic force of the medium.
In conclusion both beetle wave and electron wave are standing wave which is co- existence and moving with the matter (beetle and electron). Anyway there are two different points between them; first, the former is a 2-dimension wave, while the latter is a 3-dimension wave. Second, beetle wave is a vertical transverse of water surface wave, while electron wave is a rotational transverse wave in vacuum medium.
5) Particle wave vs. light wave. Up to now, we have talk a lot about particle wave; here we will get a better understanding of it by comparing with photon, which is a wave packet of light wave. And first we will summarize about what a photon is! (Please see detail explanation in CEMT.)
Let us start with the Mechanism of light wave. We have learned in school that light is emitted from an exited atom, but under the concept that “vacuum space is empty” it is impossible to explain how it could be done. Instead if we accept the concept “existence of vacuum medium” then it is easy to understand how light is emitted!
In
diagram fig. 2(a), when an electron in an atom was exited by energy E
(say, from incoming electromagnetic wave) and move from its normal state
of lower energy to excited state of higher energy. Immediately the
exited electron will jump back from unstable (excited) state to its normal
(stable) state! Because the “transition time” is very short, so the
jumping back electron will transfer its impulse force’s with energy
E back to the surrounding vacuum medium. This makes the disturbed
vacuum medium oscillates and radiate out as a “wave packet” of photon
from the atom with a recoil momentum ![]() .
.
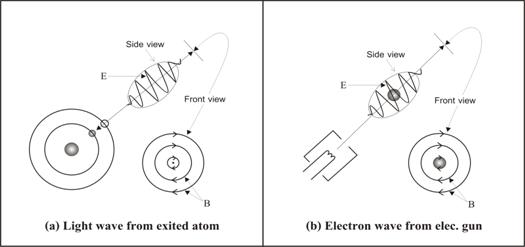
Figure 2 Light wave vs. particle wave
In section 4 we already talked about the Mechanism of particle wave (electron wave) which was shown now in diagram fig.2 (b). Here we are going to compare particle wave with photon as follow.
a) Both photon and particle wave are wave packet of the same one common transverse electromagnetic wave. In both diagrams, electric field E is a radial vector (side view), while magnetic field B is as a rotating vector (front view).
b) While photon is a free wave packet which propagates with the velocity of light, particle wave is a standing wave packet moving together with the particle.
c) Both photon and particle wave were created by a moving electron! If the moving electron is accelerated, then photon was generated, while a uniform moving electron creates particle wave.
d) From the reason of c) we often called photon as “acceleration or far field” which will radiate after it was created. Also particle wave was usually called “velocity or near field” which will not radiate, but co-moving with the moving electron!
6) Mathematical formula for particle wave. In section 4, we have explained the mechanism of particle’s wave philosophically, now we will see how it works mathematically, i.e. de Broglie wave relation (1) below. Historically [8], de Broglie wave relation, is not just a hypothesis as we know today. Louis de Broglie had derived it in his Ph.D. thesis (which Einstein had recommended the award) and later was awarded the Nobel Prize!
![]() ….. (1), [where λ =
particle wave’s length, h = Plank constant, p =momentum].
….. (1), [where λ =
particle wave’s length, h = Plank constant, p =momentum].
Nowadays, almost all text books do not talk about the derivation’s process because physicists think that it is wrong, so they accept only the output! But now we will see that the derivation is still correct (and it is corresponds to the concept of vacuum medium wave which we will talk later) and below is the original derivation.
6.1) Original derivation
of de Broglie wave formula. The crucial point in De Broglie derivation is that he assuming that
photon
has a certain rest mass![]() ! In summary, he started with
photon rest energy observed in its rest frame (achievable for
! In summary, he started with
photon rest energy observed in its rest frame (achievable for![]() ), as in (2) and it
has some characteristic
vibration
described by (3) below.
), as in (2) and it
has some characteristic
vibration
described by (3) below.
![]() …… (2),
…… (2),
![]() …. (3).
…. (3).
Now consider the same vibration as observed in laboratory frame in which the photon moving with speed v, and using Lorentz transformation, we have
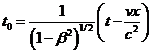 …… (4) (where
…… (4) (where![]() ), then the
disturbance described by
), then the
disturbance described by
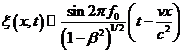 …… (5), or
…… (5), or ![]() …… (6).
…… (6).
Equation (6) is a wave with frequency f and wave speed (phase velocity) w,
where![]() …..(7),
and
…..(7),
and ![]() …..(8).
…..(8).
Note that the total energy of the
photon
measured in laboratory frame ![]() then
then
![]() ….. (9).
….. (9).
The wave disturbance described by (6) has a characteristic wavelength λ defined by the
ratio of the wave speed w to the
frequency f; 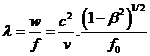 ……. (10).
……. (10).
Making use of
equation (2), the relation ![]() and equation (10), finally we get de
Broglie wave relation
which applicable for
particles with rest mass as (11) below.
and equation (10), finally we get de
Broglie wave relation
which applicable for
particles with rest mass as (11) below.
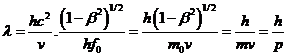 …….. (11).
…….. (11).
Note that the above derivation is “Nonrelativistic treatment of de Broglie waves” De Broglie applied his relativistic treatment of wavelength for photons to particles of nonzero rest mass. The wave nature of particles of nonzero rest mass can also be described consistently with a nonrelativistic theory, a fact of vital importance in allowing simple solutions of many quantum-mechanical problems. (This means that we use m in (11) as nonrelativistic mass of the particle considered!)
6.2) Improved derivation of de Broglie wave formula. Armed with a physical concept of wave- packet of vacuum medium, now we will improve the derivation of the conventional abstract concept (of particle wave) by using the original de Broglie’s derivation as a guideline. Then what we got is a more rational derivation with its physical meaning of de Broglie waves as below.
a) When a particle with rest mass ![]() (not photon rest mass
as in the previous section) moving with a uniform velocity v, it
will disturb
the surrounding vacuum medium and then creating a particle
wave packet (which is the co-moving rotational standing
wave) along with it.
(not photon rest mass
as in the previous section) moving with a uniform velocity v, it
will disturb
the surrounding vacuum medium and then creating a particle
wave packet (which is the co-moving rotational standing
wave) along with it.
b) Because the total
energy of the moving particle is![]() , so its kinetic
energy is equal to
, so its kinetic
energy is equal to![]() . Then this
amount of kinetic energy appeared as the energy of the created wave
packet!
. Then this
amount of kinetic energy appeared as the energy of the created wave
packet!
c) But
remember that the created (co-moving) wave packet could not
be existed alone without the original bare (rest) particle, so when we consider
its energy we must include the energy of the bare particle which is co-moving
with wave packet. That is the overall energy of the particle wave
packet is equal to![]() , which is the same thing as we
view the total energy of the moving particle without bothering
about its composition!
, which is the same thing as we
view the total energy of the moving particle without bothering
about its composition!
d) Now consider the energy of the particle wave packet which is as (12) below
![]() …… (12),
and it could be write as
…… (12),
and it could be write as ![]() or as
or as
![]() …… (13),
which has the same form as (2) but with different
meaning!
…… (13),
which has the same form as (2) but with different
meaning!
While
![]() in (2) is
the rest mass of the photon,
in (2) is
the rest mass of the photon, ![]() in
(13) is the rest mass of the particle! Accidentally, what we got is similar to
the concept of “Compton effect”, which states that “In general
the energy of a photon whose wavelength is equal to the Compton wavelength of a
particle is just the rest energy of that particle”.
in
(13) is the rest mass of the particle! Accidentally, what we got is similar to
the concept of “Compton effect”, which states that “In general
the energy of a photon whose wavelength is equal to the Compton wavelength of a
particle is just the rest energy of that particle”.
e) Finally, we could derive de Broglie derivation process similar to the procedure above (form equation (2) to (11)), together with some additional changes in the interpretation (i. e. we start with the co-moving particle wave packet of vacuum medium, instead of the photon concept). Lastly, what we got is a better de Broglie wave relation as in equation (11) as desired!
7) Better view of Schrödinger equation. In classical mechanics, if we want to find the solution for a moving particle we will use Newton’s law of motion. In electromagnetism, we obtain solution for electromagnetic wave by using Maxwell equations. But for quantum mechanics, Schrödinger wave equations (14) were used to find the solution for subatomic particle such as electron etc!
![]() …. (14),
…. (14),
Anyway, this derivation of Schrödinger equation could not be done from fundamental law, Schrödinger derived it by “making use of some deep formal analogies between optics and classical particle mechanics” [8’]. And because it is a wave equation which was used as the “dynamics equation for particle’s motion”, so it requires additional interpretation related to “particle’s aspect” i.e. “wave function Ψ ”, which was defined to be the “probability for finding the particles”, and also the probability must be conserved [3’].
Now we know that actually particle wave is vacuum medium wave. And we have learnt from CEMT that electromagnetic wave is also vacuum medium wave, but different aspects of the same one vacuum medium wave! So it is easy to derive Schrödinger wave equation in the same way as was done with electromagnetic wave! Here, we will use David Bohm’s derivation [3’’] as the guide line (the only difference is that his derivation was from an abstracted wave’s concept, while for the author’s one is from a realistic wave with philosophical idea behind!)
New derivation of Schrödinger equation. As mentioned in section 4 that electron wave is standing wave which is co-moving with the electron so the suitable mathematical tool is Fourier analysis. This is because Fourier analysis enables us to represent an arbitrary function as a sum of standing plane waves of all possible wavelengths and amplitudes of electron’s wave packet!
![]() …. (15)
…. (15)
The Fourier integral
(16) is for free
electron particle
written in complex function at t =0, and the propagation vector k for electron’s wave
packet must oscillate with angular frequency, ![]() . Hence the value of Ψ
for all times is given by multiplying each j (k) by exp -
. Hence the value of Ψ
for all times is given by multiplying each j (k) by exp - ![]() ,
,
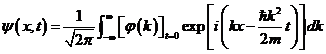 …. (16).
…. (16).
This tells us what happens to an arbitrary wave function as time passes for the case of free particle. Now to get the partial difference equation satisfied by Ψ , first differentiate equation (17) with respect to time, then we get
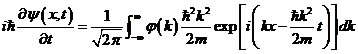 …. (17).
…. (17).
Let us now evaluate
![]() , then we get
, then we get 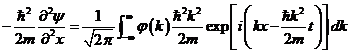 …. (18).
…. (18).
Combining (18) and (19) we obtain,
![]() …. (19).
…. (19).
This is a special case of Schrödinger equation (same as (14)) which is the standing wave packet of vacuum medium that was created and propagate with the moving particle!
8) Quantum vacuum mechanics. Up to now we have seen how to improve the mysterious basic concept of the conventional quantum mechanics with a better philosophical idea. We have explained what the mechanism of particle wave is, and shown how the de Broglie wave formula was derived. Then it permits us to derive an understandable Schrödinger equation. All these could be done via vacuum mechanics (the mechanism of vacuum medium), so it should be called as “quantum vacuum mechanics”!
Now, we have a completed quantum mechanical theory which we are looking for. Next in order to show some confidence in our new concept, we will use it to solve some unsolved basic problems in conventional QMT, i.e. waves collapse interpretation and the concept of uncertainty principle as follow.
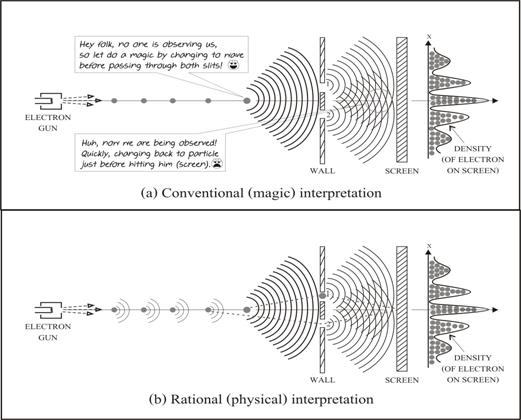
Figure 3 Wave collapse interpretations
8.1) Waves collapse interpretation. Conventionally, wave collapse interpretation in QTM is something which could explain as show in diagram fig.3 (a). But the problem is there is no explanation “how each electron converts itself into waves, passing through both slits and then the two part of waves collapse back into a single particle on screen”. Instead, armed with the concept that electron particle wave is the co-moving wave of vacuum medium, it is easy to visualize and understand how electrons do the magic as below.
In diagram fig.3 (b), all the electron particles moving together with their own created waves (i.e. electron particle is the wave source). Some of electrons pass through slit 1, while others pass through slit 2 randomly. While each electron passes through slit 1 or 2, its co-moving waves will pass through both slit 1and 2 at the same time. After passing through both slits, both the split waves will interfere each other while moving toward screen and forming to be interference pattern.
Finally, because all electron particles must move together with their own created waves (they are co-existence), then it is not surprise that all electron particles are located in the constructive interference zone. This is the reason why all electron particles are forced to arrange and forming to be interference pattern!
Note that, even though that the interference pattern which occurred on screen comes from stream of electrons, but it is not the interference between two electrons; instead it comes from one single electron which interferes with itself! Of course, one electron cannot create interference pattern, only a large amount of them could do. And this principle is also applied to photon, and which means that each photon will interfere with itself forming interference pattern!
8.2) Mechanism of the uncertainty principle! We are familiar with Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle which state that “It is not possible to determine both the position and the momentum of a particle with unlimited precision”. Instead, it could be done only according to the relation (20) below,
![]() ….. (20), where h
is Planck constant =
….. (20), where h
is Planck constant = ![]()
It was said that “the uncertainty principle protects quantum mechanics”! Heisenberg recognized that if it were possible to measure the momentum and the position simultaneously with a greater accuracy, the quantum mechanics would collapse [9]. The only question is why it is so, or what is its mechanism?
To answer the question, we will start with classical mechanics by using the guide line from “Physics” [10] with some minor change. When we deal with “wave packet” which is a portion of a continuous wave train as shown in the diagram of fig. 4 (a), then what we got is the relation between length x and wave number k is as (21) below.
![]() ….. (21),
….. (21), ![]() ….. (22),
….. (22), ![]() ….. (23)
….. (23)
If we reduce ∆x then ∆k is increase, and in the reverse when we reduce ∆k then ∆x is increase. This means that we cannot determine both the position and the wave number of a wave packet with unlimited precision! So this is the uncertainty principle in classical mechanics which is occurred due to the property of wave packet!
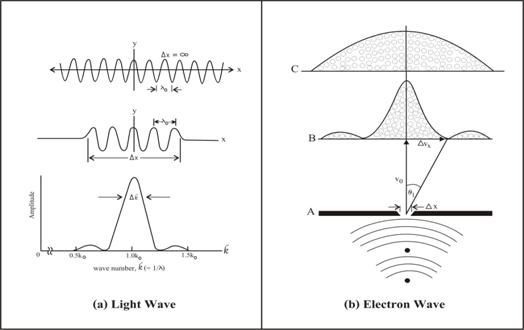
Figure 4 Mechanism of the uncertainty principle
Note that the uncertainty relation of wave packet (21) is valid for any kind of waves, so we will apply it to photon which is the wave packet of light wave by using de Broglie wave (22). (Remember that for De Broglie derivation in sec 6.1 was derived from photon.) Finally what we got is Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle as (23) or (20) above. Here we can conclude that “It is not possible to determine both the position and the momentum of a photon with unlimited precision” because it is a wave packet of light wave”!
Now we
will apply the
uncertainty relation of wave packet (21) to electron wave via “single-slit
diffraction”
experiment in the diagram of fig. 4 (b). (Please remind that electron wave is a
standing wave packet.) Consider a beam of electrons of speed ![]() pass
through the slit and create diffraction pattern as shown. We take somewhat
arbitrary value of
pass
through the slit and create diffraction pattern as shown. We take somewhat
arbitrary value of ![]() as a
rough measure of the uncertainty of our knowledge of
as a
rough measure of the uncertainty of our knowledge of ![]() and call
it
and call
it![]() . In
the diagram we could see that
. In
the diagram we could see that ![]() and
and
![]() , so the
combination of the two relations is
, so the
combination of the two relations is![]() . After
apply
de
Broglie wavelength
. After
apply
de
Broglie wavelength![]() , what we get is
, what we get is ![]() . This
means that we cannot determine both the position and the momentum of
electron with unlimited precision!
. This
means that we cannot determine both the position and the momentum of
electron with unlimited precision!
In conclusion, we could see that the uncertainty measurement of electron is due to the wave packet (of vacuum medium) created by the moving electrons. And the energy of the wave packet will guide the moving electrons to form the interference pattern. (This forming of interference pattern is the same way as what happened with double- slit). This is the mechanism of Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle!
It is interesting to note that if there were no vacuum medium, then the moving electrons cannot create electron wave. So the moving electrons will go straight pass though the slit direct to screen (without guiding from wave) and pile up as a smooth curve (due to statistical randomness, not interference) shown at the top of the diagram. So in principle, we can make a measurement of electron with unlimited precision!
9) Particle wave or matter wave? Up to now, we are quite confidence in our new “quantum vacuum mechanics”. Here we will use it for reconsidering what which conventional called as matter wave. So far, we have found that all particles in atomic level, starting from electron, proton, and neutron up to atom, have their own wave property. Anyway, the concept was extended to cover any size of particles (of matter), such as bullet golf ball up to a moving car or even a moving planet like earth, also has wave property!
Now the problem is the matter wave concept right or wrong? To answer this, we will start to consider by using Richard P. Feynman explained about “interference experiment with bullets” [9’] as shown below.
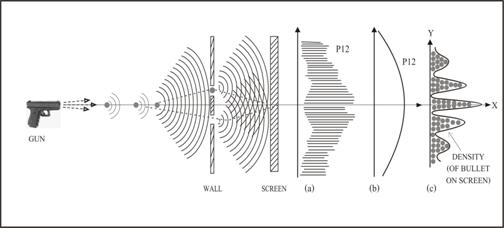
Figure 5 Interference experiment with bullets
In the diagram fig. 5 (a), is the curve shows the probability of bullets predicted by quantum mechanics, and the rapid wiggles are supposed to represent the interference pattern one get for wave of very short wavelength. But in the actual experiment we can not see the interference pattern and what we saw is only a kind of average; a smooth curve as show in fig. 5 (b). The reason is because the bullets wavelengths were so tiny that the interference pattern became very fine. So fine, that with any detector of finite size one could not distinguish the separate maxima and minima.
Now let us see, how long the de Broglie wavelength
of the bullet is!
For bullet of mass 41 g. travels at 960 m/s. its wavelength is ![]() And when we compare
it to the diameter of electron (radius
And when we compare
it to the diameter of electron (radius![]() ), we would see that it
is an incredible
tiny wavelength!
Then a new problem arises, is this realistic case or just because we think it is? To answer, we have to
consider it in more detail as below.
), we would see that it
is an incredible
tiny wavelength!
Then a new problem arises, is this realistic case or just because we think it is? To answer, we have to
consider it in more detail as below.
According to the conventional concept of de Broglie wave, it is hopeless to answer the above problem because we do not know what actually the particle wave is. But instead, armed with the new concept that de Broglie wave is a physical wave packet of vacuum medium, so we could understand and visualize it and not so difficult to solve the problem!
Technically, to set up the
experiment above, both the two slits’ width should comparable or smaller to the wavelength.
Anyway, at the same time the slits’ width must wider than the
bullets size
that is in order of millimeter![]() , which is
, which is![]() times bigger than the
wavelength! This is crazy, how could we make such slits and how could we got
the interference pattern as shown in (c)?
times bigger than the
wavelength! This is crazy, how could we make such slits and how could we got
the interference pattern as shown in (c)?
Now return to water beetle wave discussed in section 4. If we study in more detail we would found that it is not any size or at any speed of the moving beetle that could create wave! Only within a certain range of size and speed (which correspond to some mechanical properties of water’s surface tension) that enable the beetle to create the capillary wave in front. For example, the beetles have typical length less than 1 cm. and it comparable to the capillary wavelength which less than 1.7 cm. This is the reason why we never seen capillary wave in front of a moving ship! Also the moving speed of beetle is about 50 – 10 cm./s. which is faster than the minimum phase speed of wave (about 23 cm./s). If the beetles move slower than this speed, what we could found is only a highly localized disturbance of water surface; no wave pattern could be created!
Analogous to beetle wave, a moving particle should disturbed and create particle wave in vacuum medium for a certain suitable condition! This will correspond to what was called as “the domain of wave mechanics” which is a rough criterion for the applicability of ordinary particle mechanics (either Newton or relativistic) [8’’]. And it states that “the de Broglie wavelength must less than some characteristic linear dimension l of the system. For l £ λ, wave mechanics is needed”!
In conclusion, we may say that a particle wave can be created if its wavelength is comparable or longer than the diameter of the moving particle! So it is likely that de Broglie wave could be found only in the realm of microscopic (atomic) world, but not in macroscopic one. Then we should limit de Broglie wave to “particle wave” rather than “matter wave”, shouldn’t we?
10) Classical mechanics vs. quantum mechanics. Up to now, we have only talked about quantum mechanics; here we will see how the unfamiliar quantum mechanics relate to the familiar classical mechanics which we use in our daily life as follow;
First, let us start with a classical mechanics concept of Newton law of motion used for the trajectory of gun’s bullets as show in the top diagram fig.6. In the experiment, stream of bullets pass through both slits, then we got the probability of them (P12) as shown in (b). If one of the two slits was closed, then we will get the probability (P1) or (P2) as shown in (a).
Second, we deal with a classical mechanics concept of wave motion as show in middle diagram fig.6. In this experiment, if we close one of the two slits, then what we got is the intensity of wave, I1 or I2 as shown in (a). And if we add I1 with I2, then we get I1+2 as show in (c). But if we open both slits, then we will get interference pattern of intensity I12 as shown in (b).
[Note, actually the light wave of just talked above is not continuous, it is photon (wave packet of light) as shown in fig. 2(a). And the experiment result is the same as in the second case! The difference is that the interference pattern of intensity (of light wave) could equally call as probability of light particles (photons). Anyway, for simplicity here we will limit our consideration to the continuous wave.]
Third, now we will deal with electron wave-particle duality as show in the lower diagram fig. 6. And what we got is the interference pattern of probability (P12) of electrons (b) like the photon case. Also if we close one of the two slits, then what we got is the probability (P1 or P2) of electrons wave as shown in (a), while the sum of them is (P1+2) as show in (c).
Fourth, now we will compare in more detail about the detection result between classical particle mechanics (first case), classical wave mechanics (second case) and quantum mechanics (third case) as below.
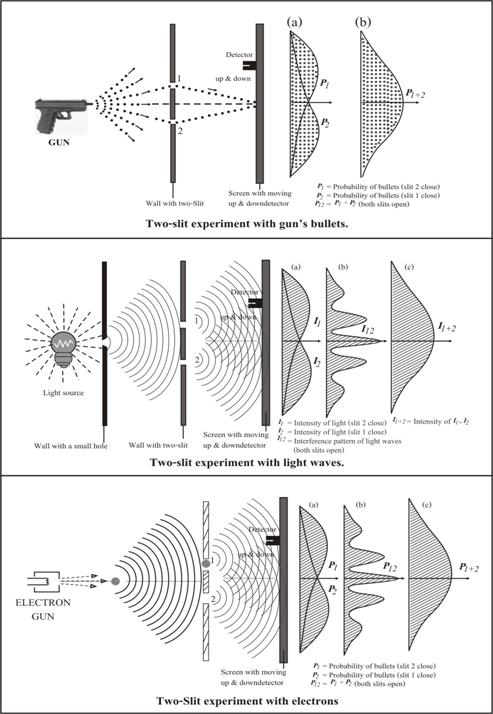
Figure 6 Classical mechanics vs. quantum mechanics
Classical particle mechanics - Total probability of bullets;
If one of the two slits close, ![]() … (p).
… (p).
Classical wave mechanics - Total intensity of light wave;
If
one of the two slits close, ![]() … (w).
… (w).
If
both the two slits open,
![]() … (w’).
… (w’).
Quantum wave-particle mechanics - Total probability of electrons;
If one of the two slits
close, ![]() … (q).
… (q).
If
both the two slits open, ![]() … (q’).
… (q’).
[Where ![]() are wave
amplitudes via slit 1 and 2, and
are wave
amplitudes via slit 1 and 2, and ![]() are
probability amplitudes
are
probability amplitudes
via slit 1 and 2 respectively]
Fifth, from equation (w), (w’) and (q), (q’), we can rearrange and what we got are
![]() …..(s),
…..(s),
![]() …..(s’).
…..(s’).
[Where Ө is
the phase difference between ![]() and
and
![]() ]
]
The last term in (s) is the interference term which arisen from wave property of light wave, while the last term in (s’) is the interference term which arisen from wave property of electron!
Lastly, if electron particle has no wave property, then (s’) will reduce to the same form of (p), which is the probability of bullets, and Newton classical mechanics could be applied. So we could say that in classical mechanics we deal with particle and wave separately, while in quantum mechanics particle and wave (wave-particle duality) being considered together!
In conclusion, Newton classical mechanics (with empty space concept) was used to handle normal particle such as a moving gun’s bullet, in which the existence of vacuum medium has negligible effect. In contrary to quantum particle such as a moving electron which creates a co-moving wave of vacuum medium, so quantum mechanics was needed to explain its behavior. Anyway, in an abstract empty space (or vacuum medium effect was neglected), then the complicate quantum mechanics could be replaced by the simple Newton mechanics!
11) Physical meaning of Planck constant. Up to now, we would notice that Planck constant h, is always involved in QTM. Conventionally, it is a proportional constant, which was derived from “black body radiation”. And it was used by Einstein to link photon energy E to its frequency f in “Einstein’s photon theory” by the relation (24), which also corresponds to Einstein mass-energy relation (25) below.
![]() …… (24),
…… (24),
![]() …… (25),
…… (25),
![]() …… (26).
…… (26).
Anyway, we do not have any idea about physical meaning of this Planck constant h, but armed with the concept that photon is the wave packet of vacuum medium, then it is not difficult to understand what it is as follow;
Start from section 6, we have a photon momentum![]() , which could be
written as in (26).Then
we could see that (25) is the same as (26)!
, which could be
written as in (26).Then
we could see that (25) is the same as (26)!
Now,
armed with the concept that photon is the wave packet of vacuum medium, which
corresponds to
de Broglie
concept
for a photon with rest mass ![]() (in section
6.1). Then we could rewrite (24) and (25) and (26) as (27),
(28) and (29) below.
(in section
6.1). Then we could rewrite (24) and (25) and (26) as (27),
(28) and (29) below.
![]() …… (27),
…… (27),
![]() …… (28),
…… (28),
![]() …… (29).
…… (29).
After we combine (27) and (28)
together and using![]() , then what we
got is
, then what we
got is
![]() … (30), or
… (30), or
![]() … (31).
[
… (31).
[![]() and
and![]() ]
]
Finally, we can interpret the “physical meaning of Plank constant h” from equation (30) and (31) based on the “basic properties of the uniform vacuum medium” (please see detail in VMTE) as follow.
a) The
first two components
in the right hand side of (30) formed the momentum of vacuum medium’s wave
packet (momentum of a photon). While the third component ![]() is the distance
of one wavelength of the wave packet, so h is one unit of the
“action of wave packet of vacuum medium” and has a dimension of
Joule-second (linear momentum-distance).
is the distance
of one wavelength of the wave packet, so h is one unit of the
“action of wave packet of vacuum medium” and has a dimension of
Joule-second (linear momentum-distance).
b) Because the entire three components in the right hand side of (30) are the basic properties of the uniform vacuum medium and they are all constant, so h is constant! (Note that c is not only the velocity of light wave in conventional sense, but actually it is the velocity of wave packet which propagates in the uniform vacuum medium, so it is constant.)
c) For equation (31), the entire three components in the right hand side of (31) is constant because when m is increasing then λ is decreasing. So both h in (30) and (31) are the same one Plank constant!
d) Finally, we return to the mechanism of light wave (photon) concept in section 7, which we sew that actually it is the mechanism of wave packet of vacuum medium! And when we combine it with what we have talked about the Planck constant h in a), b) and c), then we may conclude that the physical meaning of Plank constant h is one unit of the “quantum action of the vacuum medium’s wave packet” created by the changing state of an electron in an excited atom of the “black body radiation” phenomena!
Note that for particle wave, the Planck constant h
in
de
Broglie wave relation ![]() (where m, v,
λ are mass, velocity and wavelength of the particle respectively) is the same
as in (30), only the interpretation is slightly different from photon. The
reason is because particle wave is standing wave packet, while photon is free
wave packet
as explained in the previous section. And we have seen that actually de Broglie
wave relation was derived from the photon concept, so if we reverse the process in section 6.1 then
we will return to (30).
(where m, v,
λ are mass, velocity and wavelength of the particle respectively) is the same
as in (30), only the interpretation is slightly different from photon. The
reason is because particle wave is standing wave packet, while photon is free
wave packet
as explained in the previous section. And we have seen that actually de Broglie
wave relation was derived from the photon concept, so if we reverse the process in section 6.1 then
we will return to (30).
12) Is energy continuous or discrete? In modern physics, it was believed that energy quantity is a discrete, not a continuous value as was told by classical theories. The reason comes from Planck’s radiation law – the quantization of energy which he assumed that atoms behave like tiny oscillators with a characteristic frequency oscillation. And the assumption behind the law is that the energy of an atomic oscillator is quantized; the oscillators emit or absorb energy E in a discrete set, defined by
E = nhf …… (32) (where the quantum number n =1, 2, 3, …¥,
h is Planck constant and f is the oscillator frequency).
Beside quantum mechanics, it was assumed that the concept of quantized energy is also true for classical mechanics such as the mechanical oscillation system of clock spring and pendulum. To support the quantized energy concept, it was explained that we can not detect the graininess (of the discrete energy) of the system because it is too small to be observed. Anyway, this is not the evidence which decide whether the assumption is right or wrong!
Now we will look in the opposite side i.e. to show that it is likely that the concept of quantized energy was limited within quantum ream and not for the classical one! And indeed we will found that it is easy to understand and to visualize how it behaves in this way, by using the concept of quantum vacuum mechanics. Here are the details.
First it is easy to visualize the between a short portion of wave train (wave packet or discrete amount) and a continuous wave train which occurred in water wave. By applying a short duration of the disturbance source such as dropping a stone in water then wave packet of water could be created, while a continuous wave train could be generated by dipping a continuous vibrating fork in water!
Analogously for electromagnetic waves, wave packet of light (photon) is a short portion of wave train of electromagnetic wave, while radio wave which is man-made electromagnetic wave is a continuous wave. The reason is because radio wave was created from a continuous varying current source (please see detail in CEMT).
Now we come back to the mechanism of light wave packet mentioned in section 5, which says that when an electron (in an atom) was in an exited state, it will jump back to the normal state. At the same instant of time, it will transfer its impulse force disturbing and vibrating the surrounding vacuum medium, then radiate as the emitting photon (light wave packet). This corresponds to Planck’s radiation law which says that the energy of an atomic oscillator is quantized. And here we can see that the atomic oscillator is not a continuous oscillator, instead it acts as an impulse oscillator. This is the reason why the energy from an atomic oscillator is quantized!
So the crucial point is in the interpretation of Planck idea, in which we must not think that the atomic oscillator is a “normal” continuous oscillator which generates the discrete energy as was misunderstood. Instead, it is the oscillator which oscillates in discontinuous (discrete) manner i.e. it is an impulse oscillator! So this atomic oscillator is not the same thing as a classical mechanics oscillating system such as clock spring and pendulum.
By the way, normally when talking about an oscillator, we usually mean a continuous oscillator both a classical mechanics oscillating system or electromagnetic oscillating system. And in our daily experience we could see both types of oscillator as mentioned in the early paragraph, thing is different in atomic ream in which only the impulse oscillator is possible!
In conclusion, because of our ignorance about mechanism of Planck’s radiation energy, so we think that the concept of quantized energy is also true for classical mechanics. Now based on vacuum mechanics concept i.e. the mechanism of vacuum medium, then we found that actually quantized energy was limited within quantum ream and not for the classical one!
13) Is quantum entanglement right or wrong? Nowadays, main part of modern physicists seems to believe in quantum entanglement (correlation), such as one electron can affect another electron simultaneously, no matter how far they are separated! This was claimed to be the nature of the conventional QTM, and a mathematical formula called Bell inequality was used for proving the idea.
Anyway, the problem is that they do not know how electron can do the magic! For me (the author), this is crazy and we will show that the true problem is because of our ignorance in the mechanism of quantum mechanics, which is then give us with misinterpretation in the theory. Here we will break the quantum magic and turn it back to the real science by using our new concept of quantum vacuum mechanics, as follow.
13.1) Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox Historically, quantum entanglement was criticized by Einstein, in which he called it as a spooky action at a distance! And this give rise to a debate between Einstein and Neil Bohr (a famous quantum physicist), via a thought-experiment on a two-particle system, called EPR paradox.
Because the conventional interpretation of quantum mechanics, in which measurement with one particle can affect the far away particle simultaneously, for Einstein this was completely unacceptable! In Einstein opinion, there should have something (attribute) hidden, i.e. hidden variable, in which we cannot observe, that responsible for the mentioned “affect”.
Anyway, there are many experiments which tried to prove hidden variable concept of the EPR paradox, by comparing to the conventional quantum entanglement. And most of the results seem to agree with quantum mechanics, not hidden variable. In order to see, whether the experiments prove is justify or not, we will consider in detail about Bell inequality which is a new concept that is not familiar to us.
13.2) Bell inequality is a mathematical tool. In 1964 John Bell had invent a mathematical formula called Bell inequality which was used to show that quantum entanglement is right, while hidden variable theory is wrong as mentioned. Here we will summarize what the Bell inequality is.
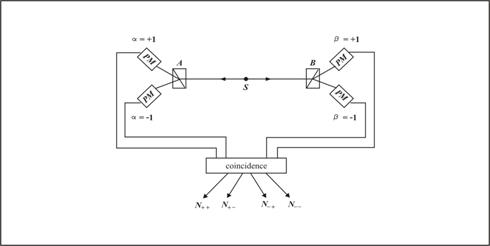
Figure 7 Bell inequality test for EPR
According to diagram fig.7,
a pair of spin-0 photons is produced in a single process from a source S. The
state of the two photons, a and b are correlated and can be described by a
two-particle wave function via quantum mechanics. Next, we assume that polarizers
at A and B can detect only two values of two types of photons i.e. (+1) for
parallel polarize photon and (-1) for perpendicular polarize photon, then
![]() for detector A
and B respectively.
for detector A
and B respectively.
To do the experiment
test, two orientations are allowed for each detector, that is ![]() and since each
detector has two possible orientations called 1 and 2, we shall denote their
responses as
and since each
detector has two possible orientations called 1 and 2, we shall denote their
responses as ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Now let us define the
quantity ![]() is what was
called as the correlation
function
of the system.
is what was
called as the correlation
function
of the system.
[where the symbol <> denote the mean value over many measured events.]
Then the BCHSH
inequality (or Bell inequality) reads ![]() And
it was proved by using Bell’s Theorem that this inequality is correspond to the
hidden variable theory [11].
And
it was proved by using Bell’s Theorem that this inequality is correspond to the
hidden variable theory [11].
When the experiment was done by counting and recording several events for some period of time, then the coincidence circuit will register the events in which two photons are detected in cascade. In this way, what we got is the four kinds of separate counts:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
And from these four kinds of separate counts we can calculate the correlation function mentioned above.
Finally, when
the experiment was done, at some value of Ө (the angle between the orientations of the
two detectors) such as
Ө =22.5
degree, it was found that the result violate the inequality, i.e. ![]() . And the result corresponds
to the prediction of quantum mechanics, i.e.
. And the result corresponds
to the prediction of quantum mechanics, i.e. ![]() then it was concluded that the hidden
variable theory is not correct!
then it was concluded that the hidden
variable theory is not correct!
Up to now, it seems everything should be alright, anyway the only one crucial problem is left; is the proves justify, or could Bell inequality is a right tool? As we have seen, Bell inequality is purely mathematical, it is not involves any physics [11’], or relate to any property of the particles in the experiment. Indeed, BCHSH inequality was criticized to be just a set of positive probability which could be derived solely on the basic of locality condition [12]. So we have to make clear that it is a proper tool used for proving the hidden-variable! Then what we have to do next is to consider the validity of the inequality.
13.3) Einstein hidden variable vs. quantum mechanics. The aim of a hidden-variable theory is to consider quantum mechanics as a statistical theory in a sense that it furnishes probability of possible events, which in reality are fixed by non-observable properties. This is analogous to classical mechanics, which incorporates random fluctuations as a property of thermodynamical system; although a discussion of individual atoms should yield complete deterministic behaviour. It would be advantageous t find similar substructures for quantum mechanics to preserve locality and determinism. Of course a theory including hidden-variables has to reproduce all the experimentally confirmed the result of quantum mechanics.
Unfortunately, Einstein had died before giving more detail about the hidden-variable. Anyway, In 1952 David Bohm had developed a thought - experiment test between quantum mechanics and the hidden-variable [13]. In the experiment, a real spin vector analogous to a classical angular momentum vector was introduced as the hidden-variable for system of two-particle with total spin zero.
It is interesting to note that Bohm hidden-variable parameter is not just an abstract one, as was done by Bell; instead, it involves with the property of the particles i.e. spin vector! In summary, the derivation of the experiment result was done in the same way as Bell‘s one, i.e. prediction probability of the spin component of particles was measured in the experiment.
According quantum mechanics, probability of the measured spin component of particles was defined as follow:
![]()
[where
![]() = spin angle
reference to z axis]
= spin angle
reference to z axis]
Next we define the average value of the spin measurement as
Correlation coefficient ![]()
And according to the hidden-variable theory,
![]()
Then the Correlation coefficient ![]()
When the experiment was done, we found that the result of the Correlation coefficient is corresponding to quantum mechanics’ prediction, so this mean that the proposed real spin vector as the hidden-variable is still not a correct one!
Anyway, by compare between the two correlation coefficients, we could see that it has indicated something interesting; there is a linear variation in the correlation of the hidden-variable case, while the correlation varies as the cosine of the angle in the quantum mechanics case. Could this reflect something about the property of the spin particle, in which we are considering?
Armed with our new concept of quantum vacuum mechanics, we could see that it will guide us to Einstein hidden-variable we are looking for as follow.
First, let us reconsider the famous Schrödinger equations (14), which is the foundation equation in quantum mechanics. Remember that it is a wave equation. And because it contains the imaginary number i, so its solution is a complex wave function [3’], for example, wave function of an electron:-
![]() [where c =
constant], which then give the probability
[where c =
constant], which then give the probability![]() , correlation coefficients
<> (mentioned above) proportional to cosine (trigonometry) function.
, correlation coefficients
<> (mentioned above) proportional to cosine (trigonometry) function.
Second, according to conventional quantum mechanics, what we have found in the previous paragraph was derived without understanding why it is so! But anyway, we also have seen that based on our quantum vacuum mechanics we found that actually the wave concept was arisen from the rotation of the moving quantum particle (that disturbed the surrounding vacuum medium)!
Third, now it is not surprise why the real spin vector (as the hidden-variable) is not correspond to quantum mechanics prediction; it is because the real spin proposed is just a classical spin concept, which not involved with any wave nature!
Finally, we could see that all the proposed hidden-variable so far is not relate to any property of the quantum particles under testing. Instead, it is just a simple classical parameter, which is not complicate as what really occurred in quantum realm. This is the reason why the experimental results using Bell inequality test do not conform to quantum mechanics!
In conclusion, armed with quantum vacuum mechanics, we could see that actually Einstein (local) hidden-variable is the quantum mechanism of vacuum medium - quantum vacuum mechanics. And it is this mechanism which responsible for the mentioned quantum entanglement via the conservation law of angular momentum between the two electrons of a total zero spin system [14]!
By the way, there is another main problem about the incompleteness of conventional quantum mechanics, in which Einstein had mentioned; it is the randomness which was told to be the nature of quantum particle. For Einstein, who believed that determinism (exact knowledge of initial condition, allow the future to be predicted exactly) is the universal characteristic phenomena, while randomness is merely due to our ignorance!
Actually, we have talked about the uncertainty principle (which stated that it is not possible to measure the momentum and the position simultaneously with a greater accuracy) and point out that it was due to the existence of vacuum medium! And if there were no vacuum medium, then in principle, we can make a measurement of electron precisely. So in this sense, we could say that the randomness was due to the hidden-variable of unobservable vacuum medium, couldn’t we?
14) Problem with
hydrogen atom model. We are familiar with Bohr model of hydrogen atom as
shown in diagram fig.8 (a) below. And the circular motion of electron for the
stationary state is at Bohr radius ![]() (calculate by using
classical mechanics), but it was criticized that it would radiate energy and
spirals into the nucleus!
(calculate by using
classical mechanics), but it was criticized that it would radiate energy and
spirals into the nucleus!
In quantum mechanics, where what we got is a better model of hydrogen atom as shown in diagram fig.8 (b). It has shown the probability location of the electron around the proton nucleus for the ground state in atom, which was calculated using Schrödinger equation. And in diagram fig.8 (c) has shown the radial probability density which is maximum at the radius r equal to Bohr radius.
Anyway, even the model in quantum mechanics, there is still no explanation why electron can stay separate from the proton nucleus, and it still depends on Bohr assumption (the postulate of stationary state)! Instead, the problem could be explained by using the concept of “vacuum medium space” (instead of conventional empty vacuum space) and “electron and proton are (something like) tiny black holes of vacuum medium”. Please see detail in VMTE.
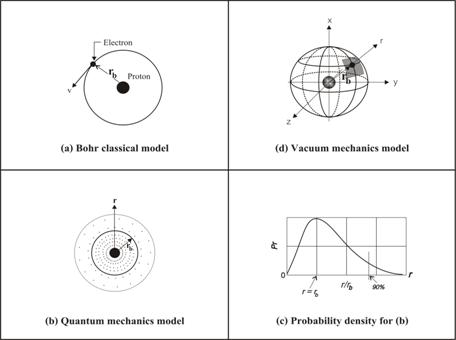
Figure 8 Hydrogen atom model
Under the concept of “quantum vacuum mechanics” we could use the model shown in diagram fig.8 (d) for explanation why “electron can stay separate from the proton nucleus and having the probability density” as shown in (a) and (b). Normally electron can move freely (even at absolute zero degree temperature) in “Bohr shell” for the reason that, it is the place where the “Coulomb attraction force” (between electron and proton) equal to the repelling force of the “vacuum medium” in between! (Detail could be seen in CEMT.
Finally we also knew that there is always a small vibration in any atom, except at absolute zero degree temperature! So any electron in any atom could not stay only within Bohr shell, instead it has the probability to move to other location out of Bohr shell when time goes on. Of course, the probability density of electron is according to wave mechanics calculated by Schrödinger equation. So what we got now is a better explanation for hydrogen atom model which is more realistic and understandable!
15) Conclusion & Discussion. Up to now, we have learnt how to improve conventional QMT by using the new concept of vacuum mechanics, i.e. the mechanism of vacuum medium. Also we have shown how a suitable and understandable model was built, what its advantage is and how it solves the existing problems in QMT!
Actually, what we have done is just “putting vacuum mechanics into quantum physics theory” and then turns it to quantum vacuum mechanics (CQMT)! So we could eliminate the mystery in QMT, turning its magic to science and make it understandable to anyone. Of course, we known that QMT is the excellent tool used for exploring the micro world, but without understanding, lead us to something crazy in the theory which we are facing now!
Nowadays, the standard model of particle physics theory, which is the main tool used for Large Hadron Collider, is based on QTM (i.e. quantum gauge field theory). Anyway, beside its successful in prediction about any (non-gravitational) process in the universe, the standard model was criticized as “an extraordinary ad hoc and ugly theory that it was clearly nonsense”. Armed with a non-mysterious CQMT would make it a better theory than it is!
Lastly, we could see that what was written in this paper is a short one, and it is not fully mathematical rigor. What we have done is just enough to give the new idea to the readers with some confidences. So what was left here should be the work of people who are involved in the matter to complete it for the virtue of academic merit and the progression of our world’s advanced knowledge!
16) References.
(Precaution; Several text books with different authors were used as the reference and each author used different pattern and different notation for the same formula. Here in this paper, the author has made some change of the original pattern and notation for the readers convenient, so please be careful!)
[1] By Nimit Theeraleekul, now presenting in www.vacuum-mechanics.com.
[2] Richard P. Feynman, “The character of physical law”, p.129.
[3] David Bohm, “Quantum theory”, p.167. For [3’], p. 85, and for [3’’] p.77-79.
[4] Jeffrey Bub, “Interpreting the Quantum World”, p. 40. For [4’] p.4.
[5] Tolstoy, Ivan, “Wave Propagation.”, p.1.
[6] Tian Yu Cao, “Conceptual Development of 20 th Century Field Theory”, p. 149.
[7] Lee A. Segel, “Mathematics Applied to Continuum Mechanics”, the first page.
For [7’] - p. 379.
[8] A. P. French and Edwin F. Taylor, “An Introduction to Quantum Physics (The M.I.T.
introductory physics series)”, p. p.55-57, for [8’] p. 65, and for [8’’] p.97.
[9] Richard P. Feynman, “The Feynman Lecture on Physics (volume III); Quantum
Mechanics”, p.1-11. For [9’] p. 1-9.
[10] D. Halliday, R. Resnick, and K. Krane, “Physics” Vol. 2 Extended Version Fourth
Edition, p. 1049-1051.
[11] Charles Ruhla, “The Physics of Chance”, p.206-208, and [11’] p.205.
[12] Tony Rothman & E.C.G. Sudarshan “Hidden Variable or Positive Probabilities?”,
arXiv:quant-ph/0004109v4 5 Feb 2001.
[13] Walter Greiner “Quantum Mechanics – An Introduction”, p. 422.
[14] John S. Townsend “A Modern Approach To Quantum Mechanics”, p. 135.
………………………..